Steps
Note - Above steps are for Android studio wizard. Sorry for eclipse developers (Please migrate to AS)
Step - 2
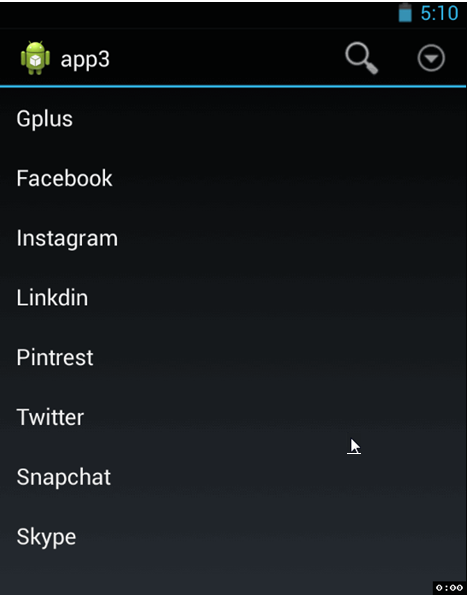
So our android wear module is added. I hope you have no issue in above steps. in the main activity or launcher activity i have created a List (basically list of my tutorials). For learning purpose you can start with same and after that you can change it is as you want. so put below code in appropriate layout files.
wear/layout/activity_list.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.wearable.view.WatchViewStub
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/watch_view_stub"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#e4e5e5"
app:rectLayout="@layout/rect_activity_list"
app:roundLayout="@layout/round_activity_list"
tools:context=".ListActivity"
tools:deviceIds="wear">
</android.support.wearable.view.WatchViewStub>
wear/layout/rect_activity_list.xml & wear/layout/round_activity_list.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.wearable.view.BoxInsetLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
tools:context=".ListActivity"
tools:deviceIds="wear_round">
<android.support.wearable.view.WearableListView
android:id="@+id/listView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dp"
android:overScrollMode="never" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_header"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_gravity="top|center"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:textColor="#52bf90"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-light"
android:text="@string/app_name"/>
</android.support.wearable.view.BoxInsetLayout>
Step - 3
List layout is done in Step -2. now let's jump to coding part where i have initialize WearableListView with Array adapter. Using GoogleApiClient i have checked if there is a connection to a android wear from an app or not. we can get all connected nodes or devices using Wearable.NodeApi.getConnectedNodes method. check below code and make sure you understand or go through it for one time so you know what is actually going on. otherwise you will get confused.
wear/java/ListActivity.java
package com.androprogrammer.tutorials;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.wearable.view.WatchViewStub;
import android.support.wearable.view.WearableListView;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult;
import com.google.android.gms.common.api.GoogleApiClient;
import com.google.android.gms.common.api.ResultCallback;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.MessageApi;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.Node;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.NodeApi;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.Wearable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ListActivity extends Activity implements GoogleApiClient.ConnectionCallbacks, GoogleApiClient.OnConnectionFailedListener,WearableListView.ClickListener {
private WearableListView mListView;
private ArrayList<String> listItems;
Node mNode; // the connected device to send the message to
GoogleApiClient mGoogleApiClient;
private boolean mResolvingError=false;
public static String SERVICE_CALLED_WEAR = "WearListClicked";
public static String TAG = "WearListActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_list);
//Connect the GoogleApiClient
mGoogleApiClient = new GoogleApiClient.Builder(this)
.addApi(Wearable.API)
.addConnectionCallbacks(this)
.addOnConnectionFailedListener(this)
.build();
initializeListItems();
final WatchViewStub stub = (WatchViewStub) findViewById(R.id.watch_view_stub);
stub.setOnLayoutInflatedListener(new WatchViewStub.OnLayoutInflatedListener() {
@Override
public void onLayoutInflated(WatchViewStub stub) {
mListView = (WearableListView) stub.findViewById(R.id.listView1);
mListView.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(ListActivity.this, listItems));
mListView.setClickListener(ListActivity.this);
}
});
}
private void initializeListItems() {
listItems = new ArrayList<>();
listItems.add("Async File Read");
listItems.add("Battery Status");
listItems.add("Volume Setting");
listItems.add("Frame Animation");
listItems.add("Video Player");
listItems.add("Circular Image View");
listItems.add("Track User Location");
listItems.add("Take Image");
listItems.add("Image Grid View");
listItems.add("Image Switcher");
listItems.add("Tabs with Toolbar");
listItems.add("Icon Tabs with Toolbar");
listItems.add("Push Notification");
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
if (!mResolvingError) {
mGoogleApiClient.connect();
}
}
/**
* Resolve the node = the connected device to send the message to
*/
private void resolveNode() {
Wearable.NodeApi.getConnectedNodes(mGoogleApiClient)
.setResultCallback(new ResultCallback<NodeApi.GetConnectedNodesResult>() {
@Override
public void onResult(NodeApi.GetConnectedNodesResult nodes) {
for (Node node : nodes.getNodes()) {
mNode = node;
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void onConnected(Bundle bundle) {
resolveNode();
}
@Override
public void onConnectionSuspended(int i) {
}
@Override
public void onConnectionFailed(ConnectionResult connectionResult) {
}
/**
* Send message to mobile handheld
*/
private void sendMessage(String Key) {
if (mNode != null && mGoogleApiClient!= null && mGoogleApiClient.isConnected()) {
Log.d(TAG, "-- " + mGoogleApiClient.isConnected());
Wearable.MessageApi.sendMessage(
mGoogleApiClient, mNode.getId(), SERVICE_CALLED_WEAR + "--" + Key, null).setResultCallback(
new ResultCallback<MessageApi.SendMessageResult>() {
@Override
public void onResult(MessageApi.SendMessageResult sendMessageResult) {
if (!sendMessageResult.getStatus().isSuccess()) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to send message with status code: "
+ sendMessageResult.getStatus().getStatusCode());
}
}
}
);
}
}
@Override
public void onClick(WearableListView.ViewHolder viewHolder) {
TextView view = (TextView) viewHolder.itemView.findViewById(R.id.row_tv_name);
String Key = view.getText().toString();
Log.d(TAG, Key);
sendMessage(Key);
}
@Override
public void onTopEmptyRegionClick() {
Toast.makeText(this, "You tapped on Top empty area", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
private class MyAdapter extends WearableListView.Adapter {
private final LayoutInflater mInflater;
private ArrayList<String> data;
private MyAdapter(Context context, ArrayList<String> listItems) {
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
data = listItems;
}
@Override
public WearableListView.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
return new WearableListView.ViewHolder(
mInflater.inflate(R.layout.row_wear_list, null));
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(WearableListView.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
TextView view = (TextView) holder.itemView.findViewById(R.id.row_tv_name);
view.setText(data.get(position));
holder.itemView.setTag(position);
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return data.size();
}
}
}
wear/layout/row_wear_list.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="8dp"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:text="Medium Text"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:maxEms="15"
android:padding="10dp"
android:ems="15"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:textColor="@android:color/black"
android:fontFamily="sans-serif-condensed-light"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:id="@+id/row_tv_name" />
</LinearLayout>
wear/AndroidManifest.xml
<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />
Please add above lines of code in manifest file of wear module. because we are using google play service to communicate. otherwise it will give error.
Step - 4
Now android wear module is ready. you can run it separately on emulator and check it. now we require a bridge which can pass android wear message to android mobile app. so when user click on list item in android wear a service get some sort of message and on the basis of that message we start appropriate activity. Using WearableListenerService we will create service which will do same for our app.
mobile/java/WearListCallListenerService.java
package com.androprogrammer.tutorials.services;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;
import com.androprogrammer.tutorials.activities.Listactivity;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.MessageEvent;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.WearableListenerService;
/**
* Created by Wasim on 08-05-2015.
*/
public class WearListCallListenerService extends WearableListenerService {
public static String SERVICE_CALLED_WEAR = "WearListClicked";
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(MessageEvent messageEvent) {
super.onMessageReceived(messageEvent);
String event = messageEvent.getPath();
Log.d("Listclicked", event);
String [] message = event.split("--");
if (message[0].equals(SERVICE_CALLED_WEAR)) {
startActivity(new Intent((Intent) Listactivity.getInstance().tutorials.get(message[1]))
.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK));
}
}
}
Step - 5
In Mobile app put below code to register your service.
mobile/AndroidManifest.xml
<service android:name=".services.WearListCallListenerService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.android.gms.wearable.BIND_LISTENER" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
That's it...
Now run wear module in android wear emulator and mobile module in device. make sure you are connected. I hope you understand the full tutorial. you can get full source code from my Github repo. if you find it helpful please share this tutorial.
Keep coding...